Building a website can be confusing, especially for beginners. This is because it is quite difficult for them to understand the difference between the domain name, website hosting and their own website.
So, are you still wondering what is a domain name and how does it work? Do not worry, we are here to break it down for you. In this article, we will explain what a domain name is and how it works. Let’s start!
A domain name is a human-friendly address, sometimes called a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) or web-address. IP addresses are created to make Internet Protocol (IP) addresses more accessible and easier to remember.
An IP address is a string of numbers assigned to each computer, much like a telephone number. IP address is arranged with random numbers like 191.124.184.129. So it is hard to remember. Unlike domain name, you only need to remember www.123-reg.co.uk. Therefore, remembering a domain name is much more convenient.
Domain name is unique, just like your fingerprint. When someone enters something in the browser, they will be taken directly to a space on the internet where you can browse your website.
Some examples of domain names include:
- Google.com
- Facebook.com
- Yahoo.com
- Wikipedia.com
Different Parts of a Domain Name
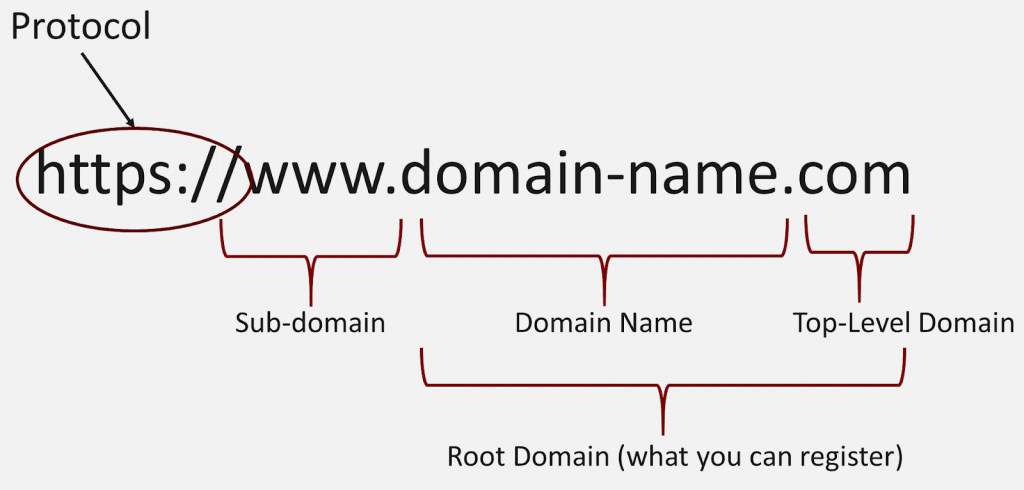
There are 3 different parts in a domain name:
1. Subdomain
This is the standard part of every domain name which is called the machine name or subdomain. However, this is optional because you do not need to enter www before the domain name in your browser to access the domain. Your domain name can be google.com.
2. Second Level Domain
The second part of the domain name is the second level domain, which is located between the subdomain and the top-level domain.
3. Top Level Domain
The end of the domain name is the top-level domain, also known as the domain extension.
The domain extension can be .com, .biz, .gov, .org and many other variations. But the most popular and well known is .com.
How Domain Names Actually Work?
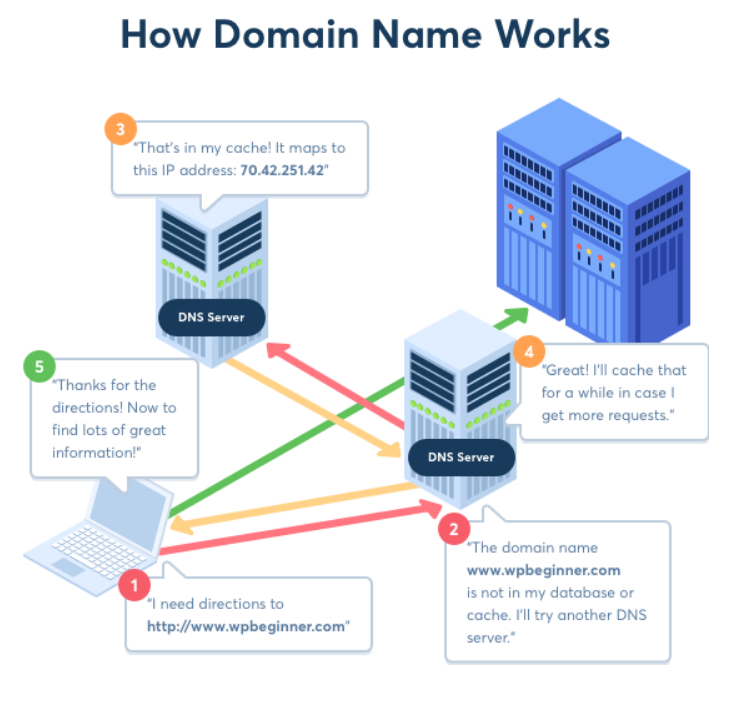
To have a better understanding about how domain names work, we will have a look on what is happening when you enter it in your browser.
1. When entering a domain name in a web browser, it will first send a request to the global network of servers that form the Domain Name System (DNS).
2. These servers then look up the name servers associated with the domain and forward the request to these name servers.
As an example, if your website is hosted on Casbay, then the name server information will be stated as below:
ns1.casbay.com
ns2.casbay.com
These name servers are computers managed by the hosting company.
3. Then, the hosting company will forward your request to the computer where your website is stored. This computer is called a web server. It had installed special software such as Apache and Nginx – two popular web server software.
4. Now, the web server will get the web page and the information associated with it.
5. Finally, the data is then sent back to the browser.