How to Configure 802.1q VLAN Tagging on RHEL / CentOS 7/8 & Fedora Interface
VLAN tagging is a way of handling a network port with more than one VLAN. VLAN tagging is use to show which packet VLAN is use for a network medium as packets. In this guide 802.1q VLAN Tagging will built on a RHEL / CentOS / Fedora framework network interface.
In addition to a parent interface, an interface is create to construct a VLAN. As they pass through the network, the VLAN interface marks packets with VLAN ID, and the return packets are unmark.
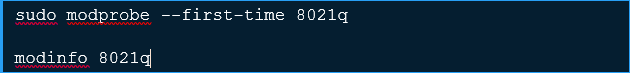
Before doing any configuration, ensure 8021q module is load.
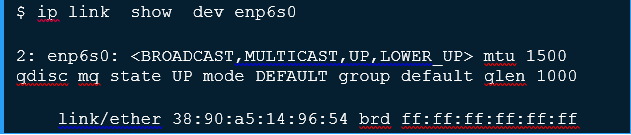
In this example, I’ll configure an enp6s0 interface on the server.
You can use the network manager command line tool – nmcli to accomplish this or directly edit network configuration files.
Manually Edit Configuration files
Edit the parent interface configuration file and set like below.
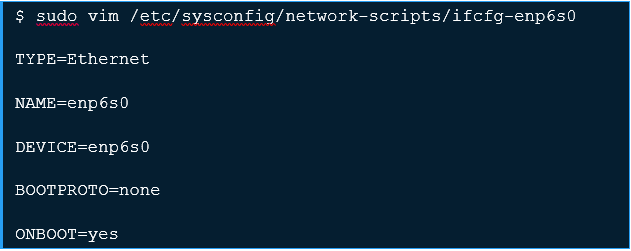
As seen above, we’ve set the interface to come up on boot and we don’t assign IP information here.
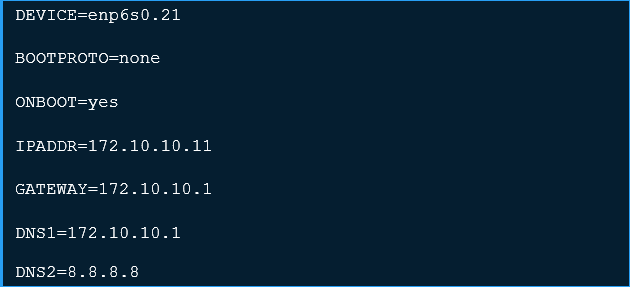
Now configure the VLAN interface. The configuration file name should be the parent interface plus a. character plus the VLAN ID number. In my setup, the VLAN ID is 21, and the parent interface is enp6s0, so the configuration file name should be:

All network configuration information is add into this file.

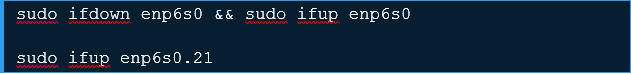
Once the update has made, restart the network service to make adjustments.

Alternatively, manually bring up the interface.
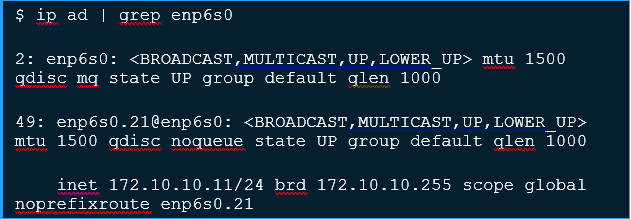
Confirm IP address information for the interface.
Using NMCLI Tool
The same configurations can done purely from the command-line interface. For this method, the NetworkManager service should be running.

Check current network configurations.

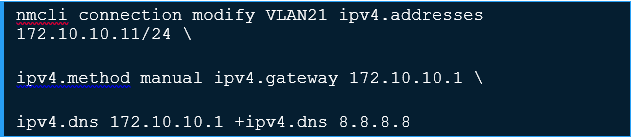
To create an 802.1Q VLAN interface on Ethernet interface enp6s0, with VLAN interface VLAN21 and ID 21, issue a command as follows:

You can then assign an IP address to the VLAN Interface.
To view all the parameters associated with the VLAN created above, issue a command as follows:

You have successfully configured VLAN tagging on an interface in RHEL / CentOS or Fedora server.